
Position-time graph of an object performing oscillatory motion with constant speed:įor an object performing oscillatory motion with constant speed, the direction of velocity changes from positive to negative and vice versa over fixed intervals of time.
On further reducing the time interval around t 0, it can be deduced that, instantaneous interval at t 0 = the slope of the tangent PQ at t 0.ĥ. Average velocity over time interval from t 2 to t 3 = slope of line CD. Average velocity over time interval from t 1 to t 4 around time t 0 = slope of line AB. Therefore, the average and instantaneous velocities are different. When the velocity of an object changes with time, slope of the graph is different at different points. Position-time graph of a particle moving with nonuniform velocity: Since it began moving, a position-time graph illustrates how far an object has gone from its beginning position at any given moment. Displacement decreases with increase in time.Ĥ. Speed is the pace at which an object moves along a path in terms of time, whereas velocity is the rate and direction of movement. The graph is a straight line with negative slope, showing that the velocity is along the negative x-axis. Position-time graph of an object moving with uniform velocity along negative x- axis: Speed is equal to the magnitude of the velocity.ģ. In this case, as the motion is uniform, the average velocity and instantaneous velocity are equal at all times. The graph is a straight line with positive slope, showing that the velocity is along the positive x-axis. Since velocity is constant, displacement is proportional to elapsed time. When an object moves, the position of the particle changes with respect to time. The position-time graph of an object moving with uniform velocity along positive x-axis: Slope of the graph is zero, which indicates that velocity of the particle is zero.Ģ. The displacement of the object is zero as there is no change in the object’s position. In such graphs, the first quantity, position, is placed on the vertical axis and the other quantity, here time, is on the horizontal axis. 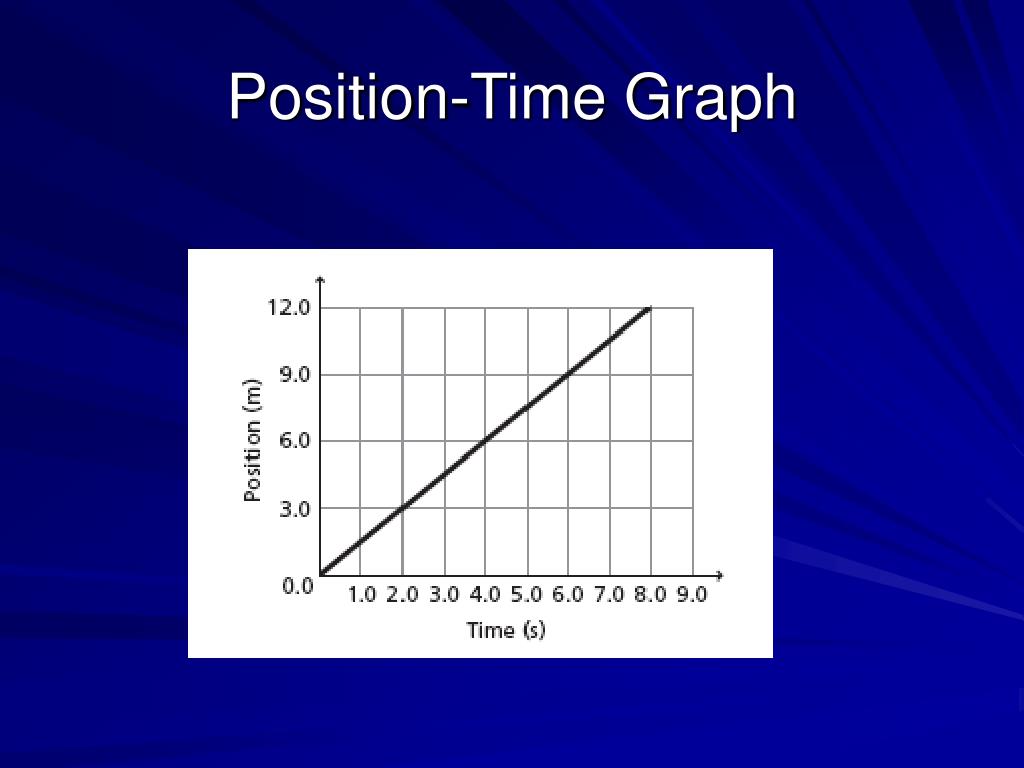
For an object at rest, the position-time graph is a horizontal straight line parallel to time axis. As its name indicates, the position-time graph shows the position of a moving object relative to the starting point at each instant of time.

The position-time graph of an object at rest:






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
